
Find out what solar panels cost in your area
Solar panels seem to be popping up everywhere these days: on solar farms, on the roofs of people’s homes, and even on cars and boats.
We know they’re used to generate electricity, but how are solar panels made in the first place?
Key takeaways
-
All solar panels have the following parts: solar cells, a glass cover, a protective backsheet, and a metal frame.
-
Solar cells are the part of the solar panel that generates power.
-
The most important raw material in solar panel production is silicon; it’s used in almost every solar panel made today.
-
Solar panels are considered a green and sustainable source of energy.
What parts are solar panels made from?
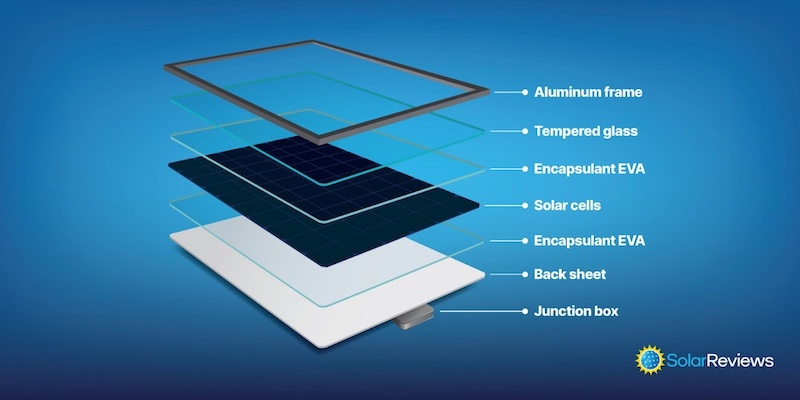
Pictured: Key solar panel components.
Here are the main components of a solar panel:
Solar cells for converting sunlight into electricity
A glass top that covers the top of the solar cells
A backsheet that protects (and insulates) the underside
An aluminum frame to hold the panel together
Let’s take a closer look at each part below:
Solar cells
Solar cells are the part of the solar panel that actually generates energy. They're specially-made electrical components that convert light into electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
Every solar panel contains many solar cells wired together, usually 60 or 72. Recently, however, the best solar panel models feature advanced half-cut solar cells; since these are smaller, twice the number can fit onto a panel.
Most solar panels use silicon solar cells made out of crystalline silicon. Other types of solar cells exist but are rarely used: thin-film solar cells, organic solar cells, and solar paint.
Glass cover
A specially-designed glass covers the front of solar panels.
The glass is tempered to make it extremely durable. It's strong enough to withstand hail impact and hurricane-force winds, providing a high degree of protection to the solar cells underneath.
The glass must also be extra clear for maximum transparency, ensuring as much sunlight as possible makes it through to the solar cells.
Glass covers can get dirty if covered by dust or soot; over time, this can affect solar power production. A bit of rainfall should wash the dirt off, but you may need to clean the panels yourself if you live in a dry environment.
Protective backsheet
The backsheet is a protective layer that covers the back of the solar panel, shielding the solar cells from the elements and any critters that might try to nibble on them from behind.
Backsheets also provide electrical insulation by preventing electric current from accidentally passing from the solar panel to surfaces it comes into contact with, such as your roof.
It also provides electrical insulation and prevents electric current from accidentally passing from the solar panel to the surfaces it comes into contact with, such as your roof.
The backsheet is made from polymer materials that are durable, lightweight, and have the appropriate insulating properties.
Backsheets are typically white. Some all-black models come with black backsheets that help give the panels a more uniform appearance. However, black backsheets tend to trap more heat and make the panel operate less efficiently.
Aluminum frame
The aluminum frame protects the edges of the panel and holds together all the layers. They are designed to handle extreme weather conditions while remaining lightweight. Many panels today use anodized black frames, as opposed to silver, because it provides a sleeker look and makes the panels less noticeable on the roof.
Module-level power electronics.
Solar panels must be attached to module-level power electronics to meet electrical safety requirements. These include microinverters and power optimizers. Some solar panels, called AC solar panels, come with microinverters pre-attached.
Why is silicon used in most panels?
Silicon is the material most commonly used in solar cells, the energy-producing part of the solar panel. In fact, the Department of Energy says it is used in more than 95% of solar panels produced today.
What is the manufacturing process?
Solar panels are produced in large, highly-automated factories using advanced manufacturing techniques.
There are usually two distinct phases: producing solar cells and assembling a complete solar panel.
Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
Solar cell production
Most solar cells are made of crystalline silicon. Here’s what the production process usually looks like:
First, silicon is melted down, mixed with either gallium or boron, and then reformed into a silicon ingot.
Next, the ingots are cut by lasers into thin sheets called silicon wafers, after which an anti-reflective coating is applied.
The silicon wafers are cut into individual solar cells and are then ready for placement inside solar panels.
The exact production process will vary depending on the type of solar cell being manufactured. Monocrystalline solar cells are made from one solid silicon crystal, while polycrystalline solar cells are made of many tiny, square-shaped crystals.
The vast majority of solar cells – including those used in locally-sold panels – are produced overseas, mainly in Europe and Asia.
Solar panel assembly
Solar panel assembly combines solar cells with all other solar panel parts to create the final product.
The desired number of solar cells are soldered together.
Next, the protective layers are added around the cells. The glass cover is attached on top, the backsheet is secured underneath, and the metal frame is placed around the entire panel.
Finally, a junction box is added to the panel to protect the electrical wires from damage. A microinverter will also be attached if it’s an AC solar panel.
Several solar manufacturers perform solar panel assembly right here in the U.S. – here are the top 5.
Are solar panels eco-friendly and sustainable?
Yes, they are! Solar panels are considered a very green and sustainable source of energy. Here’s why:
They generate clean, renewable power: Solar panels only require sunlight to operate, and they generate power without releasing any harmful emissions or waste products in the process. As such, solar panels contribute to cleaner air and reduce climate-damaging carbon emissions.
Made with abundant materials: There is no shortage of the materials used to manufacture solar panels. Both the solar cells and the glass cover are made of silicon, the second most common element on earth. Aluminum, the metal used to make the metal frame, is also very abundant.
They last a long time: Sustainable living means that we avoid using disposable items, AKA things that we use for a very short time before throwing them away. Solar panels meet these criteria – they can last up to 30 years without requiring maintenance or replacement.
Recycling programs are growing: Most solar panels retired today are sent to landfills, and many – including SolarReviews – are urgently calling for more solar panel recycling programs.
Far superior to fossil fuels: Unfortunately, most of the power we consume today comes from fossil fuels, creating air pollution and contributing to climate change. Clean and renewable solar energy is a much better alternative, which is why governments, utility companies, and homeowners are all making the switch.
Are solar panels right for your home?
Now we know how solar panels are made but do they actually work? Yes! Solar panels are designed to generate electricity; a properly designed system can produce enough power to greatly reduce your electricity bills. In some cases, this means thousands of dollars in savings every year.
Not only that, but solar panels are an excellent source of environmentally-friendly energy. Who doesn’t want to lower their electricity bills and run their home on clean power?
Zeeshan is a journalist who has covered energy, climate, and environmental topics for major news organizations. As a former member of the SolarReviews editorial team, he created content focused on solar energy and sustainable home solutions for homeowners. He has also worked in nonprofit communications and the humanitarian sector, including with Doctors Without Borders, and served as an organizer for the Pakistan Youth Climate Network. Zeeshan ...
Learn more about Zeeshan Hyder