Updated 10 months ago
Solar Panels For Home: A Beginners Guide to Residential Solar Panels
Written by
Jamie Smith

Find out what home solar panels will cost for you based on recent installations in your area
Key takeaways
-
Homeowners can run their homes using solar power instead of taking energy from the grid, which lowers energy bills and carbon footprints.
-
A home solar energy system costs between $18,000 and $20,000 before any incentives and typically saves homeowners around $1,500 annually.
-
The installation cost of solar panels and electricity bill savings depend on local electricity rates, the solar company you choose, how much sunlight your roof gets, and the rebates and tax incentives available near you.
-
On average, solar panels pay for themselves after 10 years, making them a worthwhile investment for many homeowners.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the U.S. surpassed five million in 2024 – and that number is expected to double by 2030! The growth of solar is no surprise, as this clean energy technology comes with countless benefits; it lowers your electricity bills, helps you achieve energy independence, and reduces your carbon footprint.
But, it can be hard to know exactly where to start when it comes to going solar. In this comprehensive homeowner’s guide, SolarReviews experts shed light on everything you need to know about installing a solar panel system, such as:
Home solar basics
Costs, savings, and financing options for solar
A checklist to determine if solar is right for your home
Steps of how to go solar
Top solar frequently asked questions
Home solar panel basics
Let’s start with the fundamentals of home solar, including how solar panels work, the equipment and the size system you need, and the pros and cons.
How do home solar panels work?
Solar panels produce electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. Most home solar panels are made of silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight hits the panel, the electrons in the silicon get excited and create an electrical current that flows to the system’s solar inverter. The inverter converts the DC energy made by the solar panels into AC energy, which is usable power for your appliances and devices.
Solar panels can produce more energy than your home needs. In that case, the extra solar energy can be sent back to the utility grid or stored in a battery system for later use.
There are three main types of solar power systems: grid-tied, hybrid, and off-grid systems, which we explain in the videos below.
What equipment do you need for a solar system?
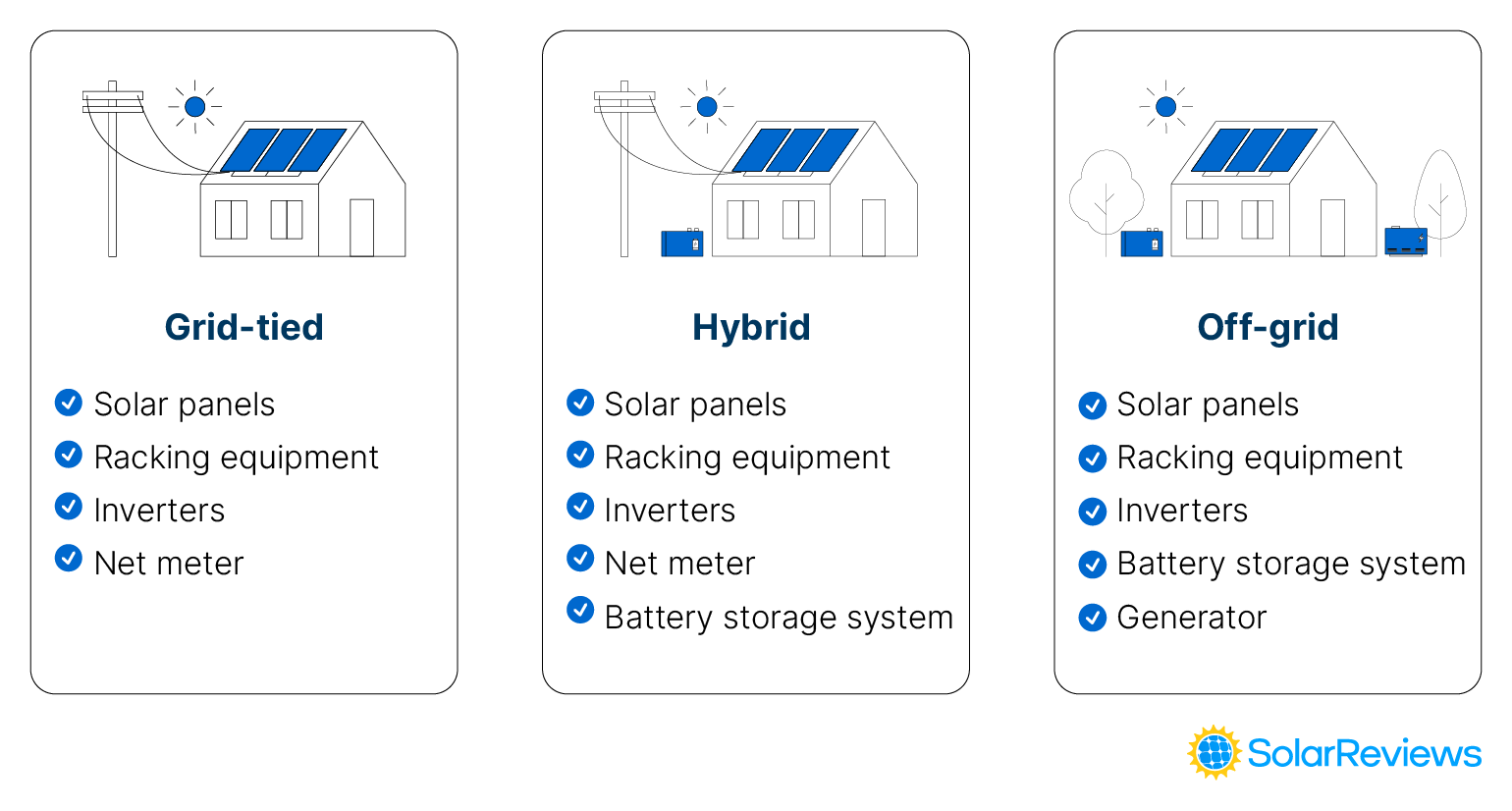
A solar energy system consists of more than just panels on your roof. There are multiple components that work together to power your home. The table below outlines each solar system component and its functionality.
Equipment | How it works |
|---|---|
Solar panels | Generate electricity from sunlight |
Racking equipment | Holds the solar panels in place on your roof |
Solar inverter | Converts the solar energy into usable electricity |
Net meter | Records how much energy your panels produce and how much energy your home uses from the utility |
Solar battery storage setup (Hybrid or off-grid systems only) | Stores any excess solar energy production for later use |
Charge controller (Hybrid or off-grid systems only) | Prevent your solar batteries from being overcharged |
What size solar system do you need?
Each home installation is unique, and you’ll need a properly sized solar system to support your energy needs.
The average solar system installed in the United States is about 7.2 kilowatts (kW) in size. That’s between 15 and 19 solar panels. However, the actual system size you need depends on your home’s roof characteristics, environmental factors, location, your energy usage, and the size of your home.
You can find out exactly how many solar panels you need by using our solar calculator, or you can solve for yourself using your home’s energy usage, the amount of sunlight your home gets, and the wattage of the solar panels used in the installation.
To calculate how many solar panels you need, use the following formula:
(Monthly energy usage (kWh) ➗Monthly peak sun hours) ➗ Solar panel output (kW)
What are the pros and cons of solar panels?
There are advantages and disadvantages to solar energy. Consider these before you make your decision:
Pros
-
Electricity bill savings
-
Clean and renewable energy source
-
Low maintenance
-
Increases home value
-
Increases energy independence
Cons
-
High upfront cost
-
Manufacturing can give off harmful emissions
-
Intermittent energy source
-
Can increase property taxes and home insurance
-
Roof characteristics and location restraints
Costs, savings, and financing for solar
Solar panels are an expensive investment, but solar incentives, rebates, and financing options can help with the burden of upfront costs. Here are a few things you need to know about paying for solar panels before you start getting quotes.
What do home solar panels cost?
In 2025, the average 7.2 kW solar installation will cost about $21,816 before any incentives are applied. In the United States, the average cost per watt of solar is about $3.03.
It’s important to remember that every household is unique, and not every home will need a 7.2 kW installation. The chart below outlines how much different size systems will cost on average before and after the 30% federal solar tax credit is applied:
System size | Average cost | Average cost (after tax credit) |
|---|---|---|
4 kW | $12,120 | $8,484 |
6 kW | $18,180 | $12,726 |
8 kW | 24,240 | $16,968 |
10 kW | 30,300 | $21,210 |
12 kW | 36,360 | $25,452 |
When you install solar, you’re paying for more than just the panels on your roof. The price of a solar installation also includes the cost of installation, racking, wiring, and even permitting. In fact, solar panels themselves only account for about 18% of the total installation cost.
How much do solar panels save?
The average homeowner can save $125 each month on electricity bills by installing solar panels. In some cases, having solar could completely wipe out your monthly bill! Depending on your utility, there may be non-bypassable fees or monthly minimum payments that solar does not cover, but you’ll still see lower bills each month.
The amount of money saved each month will depend on average utility rates in your area, your home’s power usage, the size of your system, and how your utility bills customers.
Are solar panels worth it?
In most cases, solar panels are a worthwhile investment for homeowners because of their significant benefits. Most notably,
Solar panels save $1,500 per year on average
Solar panels typically pay for themselves in 10 years or less, meaning over a decade of free energy generation
Solar panels increase home value by 6.9%, according to our data. Selling a house with solar panels can even make it easier to find a buyer!
The value of solar depends on where you are located. Good solar states with solar-friendly policies are more likely to offer incentive and rebate programs to lower the upfront cost of installation. Also, if your home is located in an ideal location with a south-facing roof and no shade, you’ll get the most out of your solar panels.
Are there incentives for installing solar panels?
The initial cost of solar seems intimidating – but solar incentives and rebates are available to help lower the financial burden of going solar. Types of incentives include:
Federal solar tax credit: A nationwide solar incentive that homeowners can take advantage of as long as they have a taxable income. The federal tax credit equals 30% of the total installation cost and is applied to the owner’s federal income taxes for the year following installation.
Net metering: Some states allow you to send excess solar energy your solar panels generate back to your electricity provider in exchange for bill credits that can cover the costs of energy drawn from the grid later.
Local rebates and incentives: Depending on where you live, your state, municipality, or local utility provider could offer incentives or upfront rebates for going solar.
How to pay for solar panels
When it comes to buying solar panels, you have a few options:
Buying in cash: Purchasing your solar panels outright with a cash purchase brings the best solar savings, no interest, and no monthly payments.
Taking out a loan: Financing your solar panels through a loan allows borrowers to retain ownership of their system without needing all the cash upfront. Solar loans come with interest, fees, and fixed monthly payments.
Using a solar lease or PPA: Getting solar panels through a lease or power-purchase agreement (PPA) requires no money down, and instead, homeowners pay the solar company monthly payments to use the energy solar panels generate.
Each financing option has its pros and cons, so be sure to consider which one is right for your personal budget carefully. Read our complete guide to solar financing options for more information.
Do solar panels increase your home value?
A 2024 SolarReviews study found that homes with solar panels are selling for 6.9% more on average than homes without solar panels. While solar panels are an attractive home energy upgrade for buyers, factors including the size of your system, the system’s condition, local electricity rates, and your location will impact just how much solar panels will increase your home’s value.
How you purchase solar panels can also factor into your home’s value, with many realtors advising clients with solar homes to ensure their systems are paid off for the easiest sale possible. Solar panels financed through a solar lease or PPA won’t add as much value to your home as a system purchase with cash or a loan and can even make selling your home more difficult in the future.
Is my home good for solar?
Before going solar, there are a few boxes you should be checking off to ensure you’re making the right decision.
1. You have high electricity bills
High electricity bills make going solar more desirable. High electricity bills mean higher solar savings accumulated each month, shortening the payback period for your solar investment.
The average electric bill in the United States in 2025 is about $144, with high rates in states like Hawaii, California, and Connecticut.
2. Your utility company is solar-friendly
Solar panels are a better investment in areas that have good net metering policies. Full-retail net metering ensures that excess solar energy will fully cover the cost of any electricity you use from the grid in the future, providing the best savings. Some utilities only offer partial credit for solar power sent to the grid.
It’s an added bonus if your utility offers other solar incentives or rebates.
It’s important to check how your utility bills solar customers and how that can impact savings before you sign a solar contract.
3. Your roof is good for solar
Home solar panels are usually installed on rooftops, meaning your roof can have a significant impact on the design of your system. Solar panels work best on roofs that are:
South-facing
Free of shade
Won’t need a roof replacement in the next 25 years
Can hold the weight of solar panels
Have at least 265 square feet of space for an installation
Your roof doesn’t have to exactly fit all of these criteria for you to go solar. However, these will ensure maximum solar energy production and operation.
Read more: Is my roof good for solar?
4. You qualify for solar incentives
Solar incentives and rebates help reduce your initial investment and make them more affordable. If you don’t qualify for incentives, like the federal tax credit or net metering, solar isn’t nearly as worth it.
For example, you need to have a taxable income to reap the benefits of solar tax incentives. So, tax benefits like the 30% tax credit might not appeal to retirees.
How to go solar
Going solar isn’t quite an overnight process. If you’re considering going solar, you’ll need to find installers, compare quotes, and wait for the installation to be complete.
1. Find trusted, local installers
Finding the right solar company can truly make or break your experience with solar panels. For starters, you can take a look at SolarReviews’ list of top installers by consumer reviews to find a company in your area.
Aside from that, try to look for an installer that fits the following criteria:
Locally owned in your area
Has been in business for 5+ years
Has consistent positive customer reviews
In-house installation crew
Holds certifications (like NABCEP)
Utilizes high-quality equipment
You’re allowed to be picky when it comes to choosing a solar company. We recommend getting at least three quotes from different companies to make an informed decision and get the best price!
2. Review quotes
Once you’ve received multiple quotes, take a close look at what each company offers. You’ll want to compare these items when looking at quotes:
System size
Cost per watt
Estimated energy production
Equipment used
Warranties
Financing options
Comparing quotes helps you make a more informed decision, get a system that fits your needs, and get you the best deal!
Learn more: How to Compare Solar Quotes and Get the Best Deal
3. Installation process
If you’ve made it this far, and feel ready to schedule a solar installation – that’s great news!
The process of getting your solar system can be a bit of a lengthy process, taking between two and six months to complete. Here’s what you can expect:
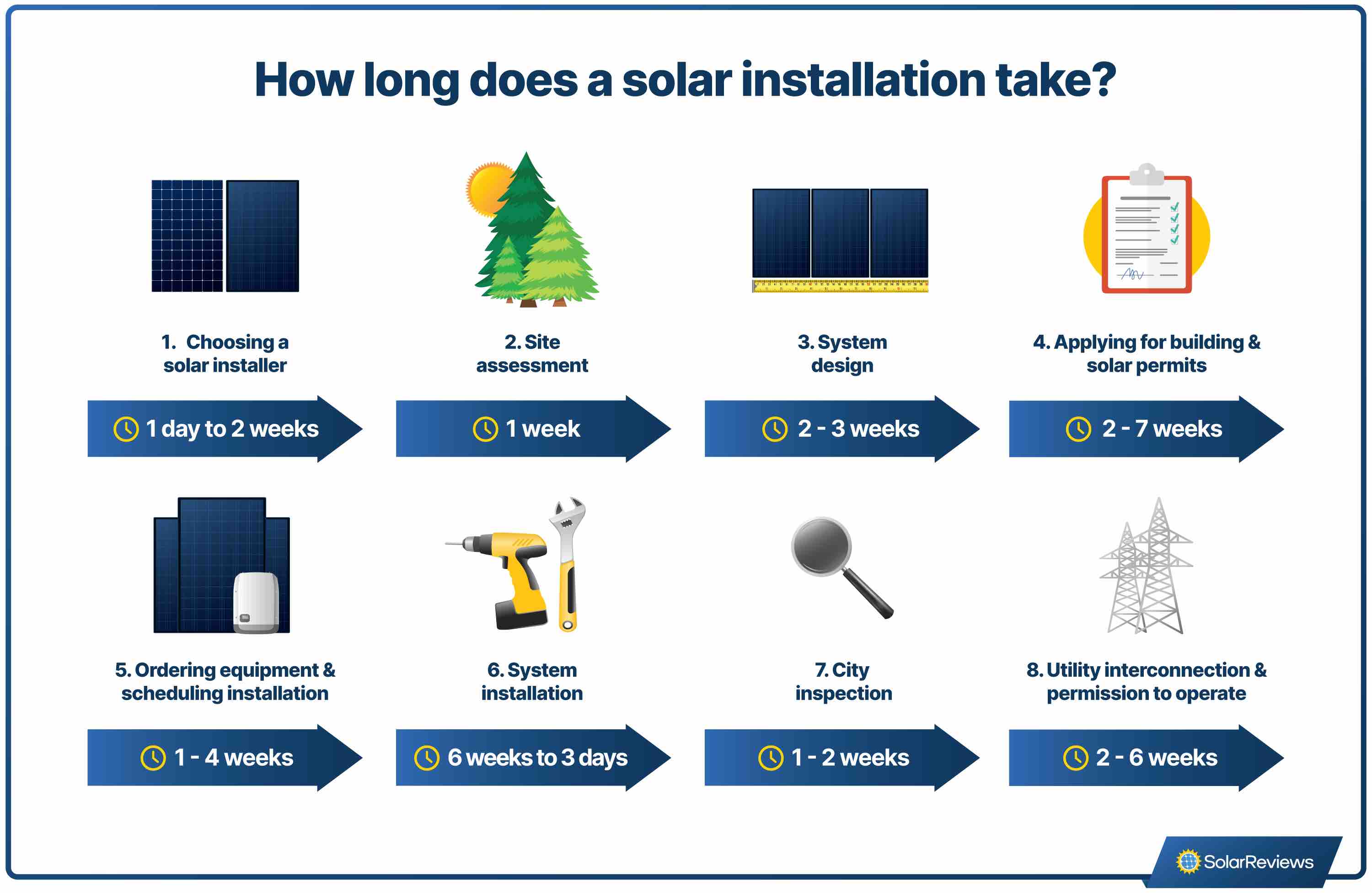
Typically, permitting and inspections are the longest parts of the installation process. If you’ve ever done home improvement projects, this comes as no surprise. Some jurisdictions use a streamlined permitting system called SolarAPP that cuts down on time, but it's not available everywhere.
A few months of waiting is worth it for a few decades of clean energy!
Solar panels for home FAQ
Jamie is a content writer and researcher with a B.S. in Communications from La Salle University, where she focused on journalism, mass media, and public relations. As a former member of the SolarReviews editorial team, she created content to help homeowners better understand solar energy and make informed decisions. Prior to joining SolarReviews, she worked at a marketing company producing long-form stories and interviews that highlighted small ...
Learn more about Jamie Smith