
Find out what solar panels cost in your area
Despite the sun being billions of years old, how humans have harnessed its energy as a renewable source is relatively new!
The utilization of solar energy has come a long way. Let’s start from the beginning and walk through all the vital points in time for the solar energy industry and beyond.
Solar energy timeline
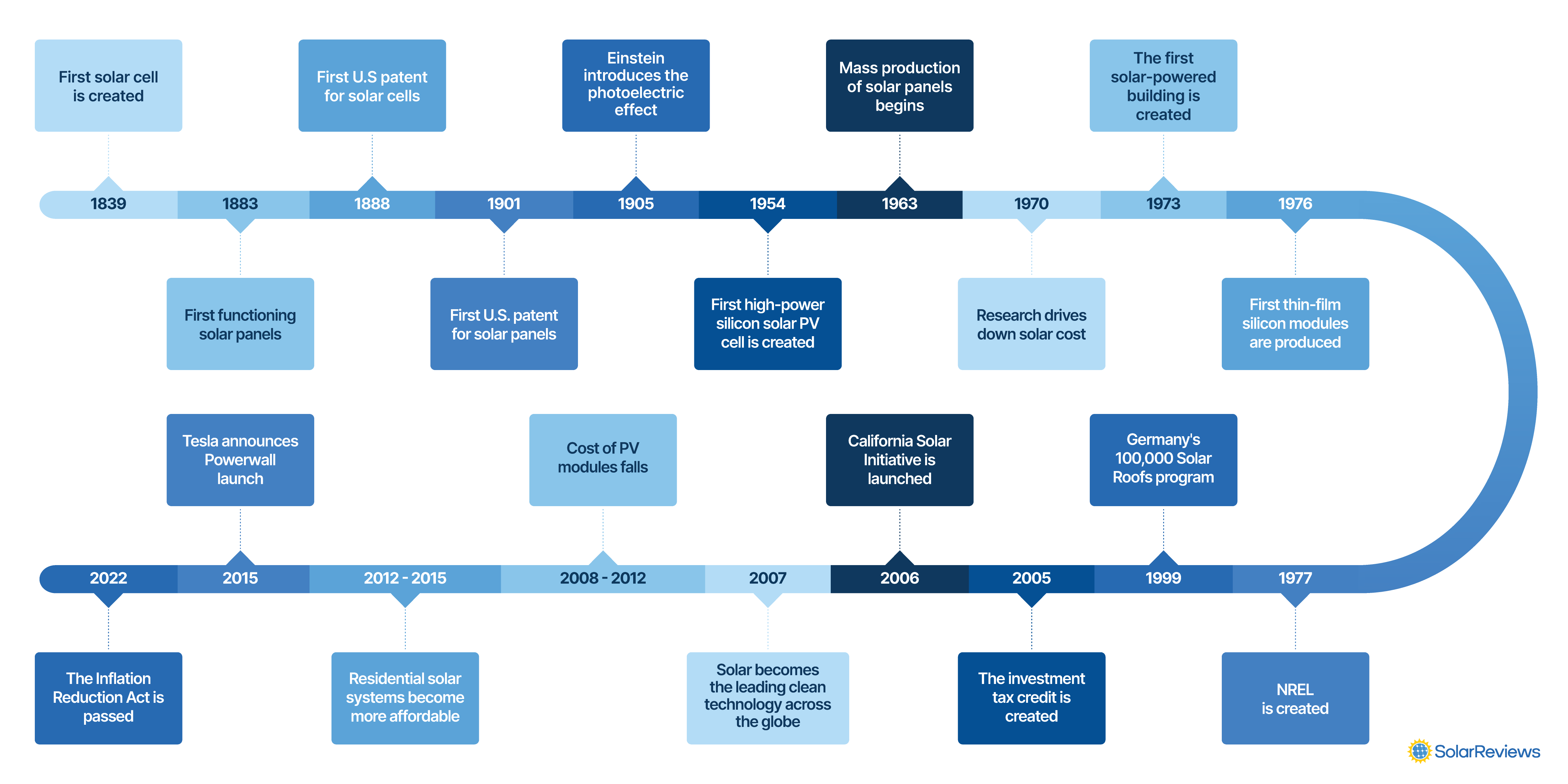
This timeline lays out the important scientific discoveries that led to determining how to utilize solar energy and how it has become more efficient and cost-effective over the years.
Interestingly, although solar panels are an excellent energy source, the United States government was originally slow to fully embrace their potential.
The first time that solar seemed like a “better option than fossil fuels” was during the oil embargo of 1973 when gas shortages were rampant within the U.S. Interest in energy independence grew and with it, the beginning of solar incentives came to be.
Years later, to help boost the economy and embrace American independence, President Jimmy Carter asked Americans to practice energy conservation and began encouraging PV technology investments. He even went as far as putting solar panels on the White House.
Historically, the U.S. lagged behind other countries in embracing solar, but this is beginning to reverse. Additionally, solar is now cheaper than coal so it now makes more economic sense to switch to renewables, like solar arrays, than to remain invested in fossil fuel plants.
Take a look at the brief history of the key events that led to solar power becoming the success that it is today.
1839 - First solar cell is created
While experimenting with metal electrodes and an acidic solution, nineteen-year-old French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel creates the first solar cell. This solar cell was known as a photovoltaic cell, which could carry an electric current from light.
Becquerel is credited with discovering the photovoltaic effect, which is how a solar cell operates.
1883 - First functioning solar panels
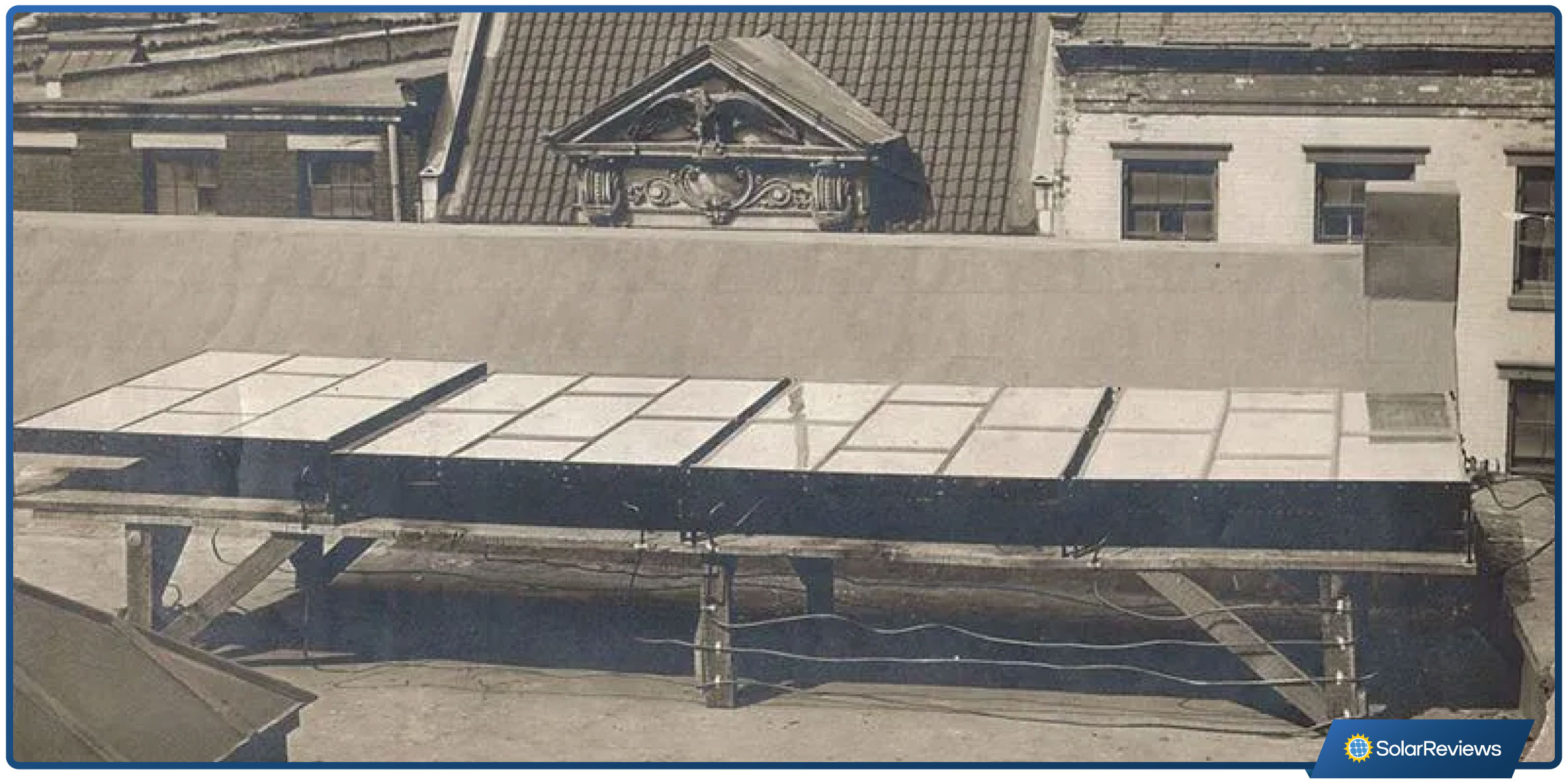

First functioning solar panels on a New York City rooftop. Source: Smithsonian Magazine
Charles Fritts, an American inventor, created the first functioning solar modules with solar cells made from selenium wafers. A man named Willoughby Smith discovered that selenium was photovoltaic.
The first solar panels were installed atop a New York City rooftop but were very inefficient, with an energy conversion rate of only 1%.
1888 - First U.S. patent for solar cells
Edward Weston received the first U.S. patent for a “solar cell,” which helped garner more interest in solar research – ultimately leading to more efficient solar panels.
1901 - First U.S. patent for solar panels
At the turn of the 20th century, Nikola Tesla received the U.S. patent for “the method of utilizing, and apparatus for the utilization of radiant energy.”
In simpler words, the first U.S. patent for solar panels!
1905 - Einstein introduces the photoelectric effect
World-renowned physicist Albert Einstein published a paper on the theory behind the “photoelectric effect,” which officially proved how the sun creates energy through solar cells. This paper went on to win the Nobel Prize in 1922.
1954 - First high-power silicon solar PV cell created
Fast forward a few decades, Gerald Pearson, Daryl Chapin, and Calvin Fuller, all of whom were physicists at Bell Labs, exhibit the first high-power silicon solar photovoltaic (PV) cell that increased energy conversion efficiency by using silicon instead of selenium wafers.
1963 - Mass production of solar panels
Sharp Corporation, a Japanese electronics company, produced a viable PV module of silicon solar cells, which led to the successful mass production of solar panels.
Japan installed a 242-watt PV array on a lighthouse – the world’s largest array at that time.
1964 - NASA launches first solar PV array
NASA launches the first Nimbus satellite with a 470-watt PV array after the successful launch of Vanguard I by the Naval Research Laboratory.
1970s - Research drives down solar cost
A rise in solar research drove PV costs down a whopping 80%, allowing for different solar panel uses to be tested and adopted. At the time, these were mostly for off-grid use.
1973 - First solar-powered building is erected
The University of Delaware builds “Solar One” – one of the world’s first PV-powered buildings. The building was powered by PV panels and solar thermal energy combined.
1976 - First thin-film silicon modules are produced
Electronics company Kyocera begins production of thin-film silicon ribbon crystal solar modules. The creation of these modules helped to simplify the manufacturing process.
1977 - NREL is created
The U.S. Department of Energy establishes the U.S. Solar Energy Research Institute in Golden, Colorado. This organization is known today as the National Renewable Energy Laboratories (NREL), and it is in charge of renewable energy research for energy independence.
1999 - Germany’s 100,000 Solar Roofs program
This German program, established in 1999, supported the installation and expansion of PV systems larger than 1 kilowatt (kW). The $500 million dollar project was pivotal in developing a viable residential solar industry. Japan had a similar subsidy program for 70,000 roofs a few years prior.
2005 - Birth of the investment tax credit
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 created a 30% investment tax credit (ITC) for commercial and residential solar energy systems. The Tax Relief and Health Care Act of 2006 helped to extend this credit.
This is what we know today as the federal solar tax credit—the biggest incentive in the United States for homeowners and businesses to go solar.
The solar tax credit has its own history, and since 2005 has been extended and revamped a number of times.
2006 - California Solar Initiative
The California Public Utilities Commission launched the California Solar Initiative (CSI), a 10-year, $3 billion solar subsidy program. The funding went towards solar incentive programs in California for low-income single and multi-family homes.
The CSI program was well-received by the market, with a higher–than–expected application volume. It closed in 2016.
2007 - Solar becomes the leading clean technology across the globe
The late 2000s was a crucial time for the growth of solar energy. Global investment in clean energy exceeds $100 billion, with solar energy as the leading clean energy technology for venture capital and private equity investment. The solar tax credit helped to create unprecedented growth in the U.S. solar industry from 2006 to 2007.
The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 included an eight-year extension of the federal tax credit, eliminated the monetary cap for residential solar electric installations, and allowed utilities and companies to qualify for the tax credit.
2008 - 2012 - Cost of PV modules falls
During this time, the global cost of solar modules falls from approximately $5 per watt to $1 per watt. This is mainly due to strong subsidies in Germany and new subsidy programs in Spain, Italy, and Australia.
2012 - 2015 - The cost of residential solar systems becomes affordable
Residential solar system installations become cost-effective for the average American household. From 2011 to 2012 alone, the average price of residential solar fell from $6.62 per watt to $4.67 per watt.
By 2015, the price decreased even further to $3.36 per watt, leading to more residential solar power being installed in the U.S. in 18 months than ever before.
2015 - Tesla announces Powerwall launch

Image courtesy of Tesla, Inc.
Elon Musk, the chief executive of Tesla Motors, announces the company’s entry into the energy market.
The first Tesla Powerwall was unveiled as a lithium-ion storage product for homeowners. At the time, the Powerwall cost the astonishingly low price point of $3,500 – making it possible for average American households to store solar power generated during the day for use at night.
Tesla has released four variations of Powerwall models since 2015.
2022: The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) passed
The passing of the IRA in 2022 was one of the most transformational clean energy policy approvals in U.S. history.
The policy extended the federal solar tax credit until the end of 2034. It also provided billions in funding to state energy offices to expand rebate and incentive programs, as well as incentives to increase domestic solar manufacturing.
2025 - The best time to install solar panels on your home
Now is the best time to save by installing solar panels on your home. The federal tax credit ensures you save on your installation by 30%, and solar costs are more affordable than ever! Use our free solar calculator to find out the costs, incentives, and returns you would get by installing solar panels.
Solar power today
The utilization of solar power has passed many milestones since its inception. The growth of residential solar was slow at first but is quickly gaining traction due to lower costs and its superiority over fossil fuels.
Here are some of today’s top solar industry highlights:
The average cost of a residential solar system is between $16,500 and $21,000 before incentives.
Some of the best places to go solar in the U.S. are: Massachusetts, Colorado, Washington D.C., and Maryland.
Solar loans, leases, and power-purchase agreements are all financing options you can choose from to get solar up on your roof.
California ranks #1 for the solar market in the U.S., with over 46,874 Megawatts (MW) of solar currently installed in the state.
It is reported that more than 92% of residential installers are also offering energy storage installations.
For more interesting facts about solar energy: 10 fun facts about solar energy
Jamie is a content writer and researcher with a B.S. in Communications from La Salle University, where she focused on journalism, mass media, and public relations. As a former member of the SolarReviews editorial team, she created content to help homeowners better understand solar energy and make informed decisions. Prior to joining SolarReviews, she worked at a marketing company producing long-form stories and interviews that highlighted small ...
Learn more about Jamie Smith