
Find out what solar panels cost in your area
You’re curious about renewable energy, and you’ve heard of solar panels - but you’re not sure what a solar array is. Worry not, you’re in the right place. In this article, you'll learn everything you need to know about solar arrays, how much a solar array will cost, and whether they're right for your home.
Key takeaways
-
A solar array is a collection of solar panels, wired together into a circuit.
-
A solar array that can power an average household would require between 13 and 21 solar panels.
-
Solar arrays generate DC power; it must first be converted into AC power using solar inverters before it can be used in your home.
-
Solar array + balance of system components (including solar inverter) = Complete solar power system.
-
A complete solar panel installation costs between $18,000 and $20,000 before incentives; of that, the solar array accounts for $5,800-$7,850.
-
Going solar can result in substantial savings, but we recommend you check if the math works out for you before taking the plunge.
What is a solar array?
Simply put, a solar array is a collection of solar panels wired together to capture sunlight and produce electricity.
Solar arrays combined with one or more solar inverters (and, optionally, a battery) become a fully functional solar power system. As part of the solar power system, a solar array generates electricity that can power a house or be exported to the grid.
What are solar arrays made of?
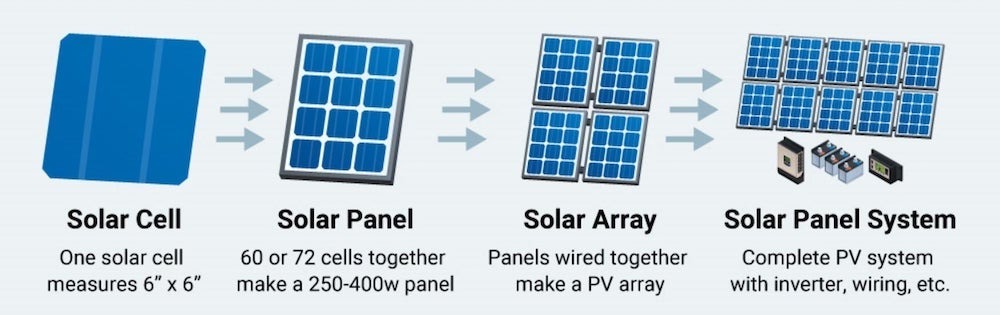
A solar array is a collection of solar panels wired together into a circuit.
Solar panels, in turn, are a collection of photovoltaic (PV) solar cells, covered with protective glass and held together with a metal frame. Solar cells are made of semiconductor material, typically silicon, that is sliced incredibly thin.
Individual solar cells generate electrical power using the photovoltaic process: photons in sunlight separate electrons from the silicon, generating an electric charge. This process is why solar panel systems are also called ‘PV systems'.
A solar array can comprise any number of solar panels depending on the required capacity:
Home array – around 20 solar panels: A typical home system has a capacity of about 6 kilowatts (6,000 watts); for such a solar array, you’d need fifteen 400 W solar panels.
Utility solar array – thousands of panels: Solar power plants, or solar farms, have power capacities of one Megawatt (1 million watts) or more, so they would have at least two-and-a-half-thousand 400 W solar panels.
Learn more: How do solar panels work?
How do solar arrays work?
Thanks to the durability of solar panels, a solar array can be used for energy production for 25 years (their warranted life) or longer. Energy production occurs without the use of moving parts, fuel, or any other kind of intervention from the owners.
Here’s a brief description of how a solar array can provide power for a home solar energy system:
Energy creation: Sunlight hits the solar cells in the array, activating them and generating Direct Current (DC) electricity.
Energy conversion: The DC power then travels to an inverter, where it is converted into Alternating Current (AC) electricity usable by the home.
Energy consumption: The 120/240 volt AC power supply is then either used on-site (i.e. by the home) or exported to the grid, from which it can be distributed to others who need power.
Where can you put solar arrays?
Solar arrays can be installed anywhere with good access to sunlight.
The most common location for a solar array installation is atop the roof of a house. It should ideally be on a south-facing section of the rooftop. In the U.S., solar arrays pointed towards the south receive the most sun, and thus generate the most power.
Another option is to install a solar array on ground mounts. This option is commonly used by solar farms or in more rural locations, where land is generally cheaper.
Solar arrays can be mounted on structures other than roofs. Solar canopies are one such option, as are solar pergolas, and even solar trees!
Heading out for the weekend? Solar arrays can also be installed atop vehicles. Solar energy has long been a popular option for RVs, while boats are starting to incorporate solar arrays, too.
Furthermore, solar arrays, paired with energy storage systems such as solar batteries, have long been used in off-grid settings such as hunting cabins.
Finally, there are more niche locations for solar arrays, such as those integrated into buildings.
How to size a solar array
Let’s assume you want a solar array big enough to wipe out your electricity bill. In that case, you may want a solar array that can produce 1,000 kWh of electricity a month, which is sufficient to cover the energy usage of an average home.
Building a solar array capable of 1,000 kWh per month would need between 13 and 21 solar panels (assuming the use of 400-watt solar panels), and require 277-450 square feet of total roof space. Speaking of square feet, the size of your home in square feet has only a little to do with how many solar panels you'll need.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
The term ‘solar array size’ describes a solar panel system’s capacity to produce electricity.
A solar array 300 watts in size, for instance, can produce 300 watts of electricity, while a solar system 6 kW in size can generate 6,000 watts (under standard test conditions).
Here are the solar array sizes you would need to produce 1,000 kWh – enough to cover average home usage – in different parts of the country:
Here are the solar array sizes you would need to produce 1,000 kWh in different parts of the country:
Region and state | Average daily peak sun hours | Solar array size | Number of panels* |
|---|---|---|---|
West: California | 6.7 hours | 5 kW | 12 |
South: Texas | 5.6 hours | 6.2 kW | 16 |
Midwest: Illinois | 4.3 hours | 7.8 kW | 20 |
Northeast: New Jersey | 4.1 hours | 8.1 kW | 21 |
*Assuming the use of 400 W solar panels
Of the four states compared above, California gets a lot of sunlight. As such, a solar array there need only be 5 kW in size (and comprise about 13 solar panels), to generate 1,000 kWh of solar power monthly.
On the other end, we have New Jersey, which receives three-fifths as much sunlight as California. Here you’d need a solar array that’s 8.1 kW, made up of around 21 solar panels, to achieve the same level of output.
Figuring out what size solar array is right for you depends on several factors such as your energy consumption, available roof space, and how much sunlight you get where you live.
Find out: How many solar panels do you need for your home?
How much do solar arrays cost?
The average cost of a complete home solar panel system in the U.S. is between $18,000 and $20,000. This figure is based on a pre-incentive cost of between $2.75 and $3.35 per watt of solar installed, as per our cost data.
Out of that, the equipment for the solar array will account for between $5,800 and $7,850.
The remainder of the total system cost comprises mainly the cost of the solar inverter(s) and the cost of the installation itself.
Learn more: Solar panel cost
Is installing a solar array a good idea?
Thanks to the low cost of solar panels, various solar incentives, and long warranties, solar arrays are a worthwhile investment for most homeowners.
Solar panel systems save the average homeowner between $900 and $1,200 a year on utility bills. This means the average homeowner will have a solar payback period of between 8 and 11 years. Then, they’ll be enjoying completely free solar electricity for another 15 years!
Your actual savings from going solar will depend on the size of your system, the cost of electricity in your region, and how many kilowatt-hours of electricity you use. It also depends on what kind of net metering policy is available in your area.
Luckily, our solar savings estimator takes all of these factors into account when determining how much you will save with solar.
Zeeshan is a journalist who has covered energy, climate, and environmental topics for major news organizations. As a former member of the SolarReviews editorial team, he created content focused on solar energy and sustainable home solutions for homeowners. He has also worked in nonprofit communications and the humanitarian sector, including with Doctors Without Borders, and served as an organizer for the Pakistan Youth Climate Network. Zeeshan ...
Learn more about Zeeshan Hyder